- Today
- Total
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
- substr
- 오블완
- Linux
- 명령어
- Optional
- barplot
- struct
- swiftUI
- sigmoid
- Observable
- Python
- SQL
- ios
- rest api
- HTTP
- decode
- scheduledTimer
- 티스토리챌린지
- SWIFT
- 딥러닝
- 시각화
- Request
- MVC
- r
- cocoapods
- 연산자
- deeplearning
- rxswift
- tapply
- ReLU
iOS 개발 기록 블로그
iOS (Swift) 리펙토링(Refactoring)과 Computed Properties 이해하기 본문
iOS (Swift) JSON 디코딩(Decoding)
func performRequest(urlString: String) { //1. Create a URL if let url = URL(string: urlString) { //2. Create a URLSession let session = URLSession(configuration: .default) //3. Giv..
crazydeer.tistory.com
지난 글에 이어 JSON을 정리하면서
MVC 디자인 패턴으로 바꾸고
그 과정에서 Computed Properties도 이해해보자.
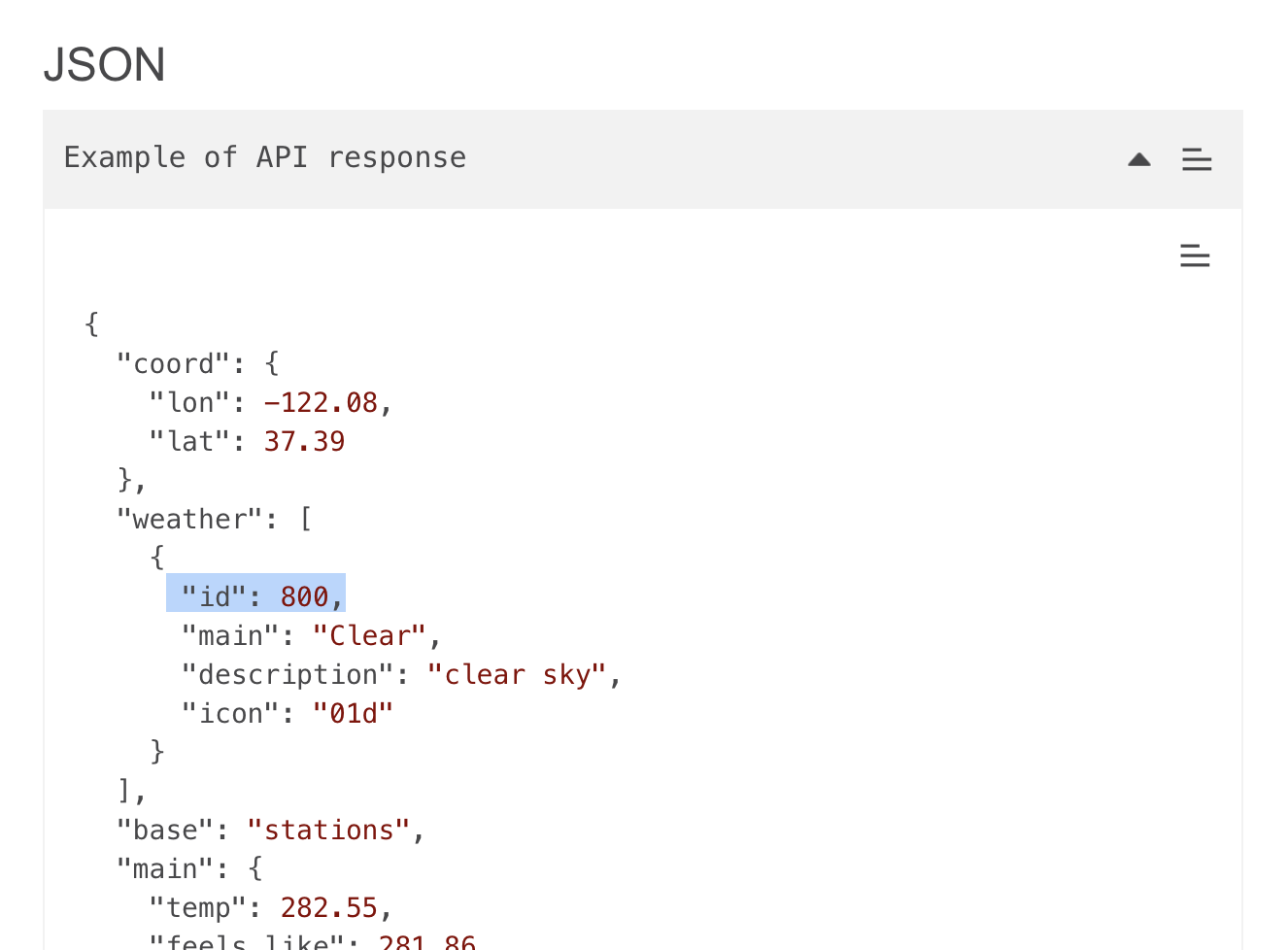
OpenWeatherAPI 문서가 제공하는 json 예시다.
여기에 id는 날씨 상태를 말하는데
이에 따라 아이콘이 변화하도록 해볼 것이다.
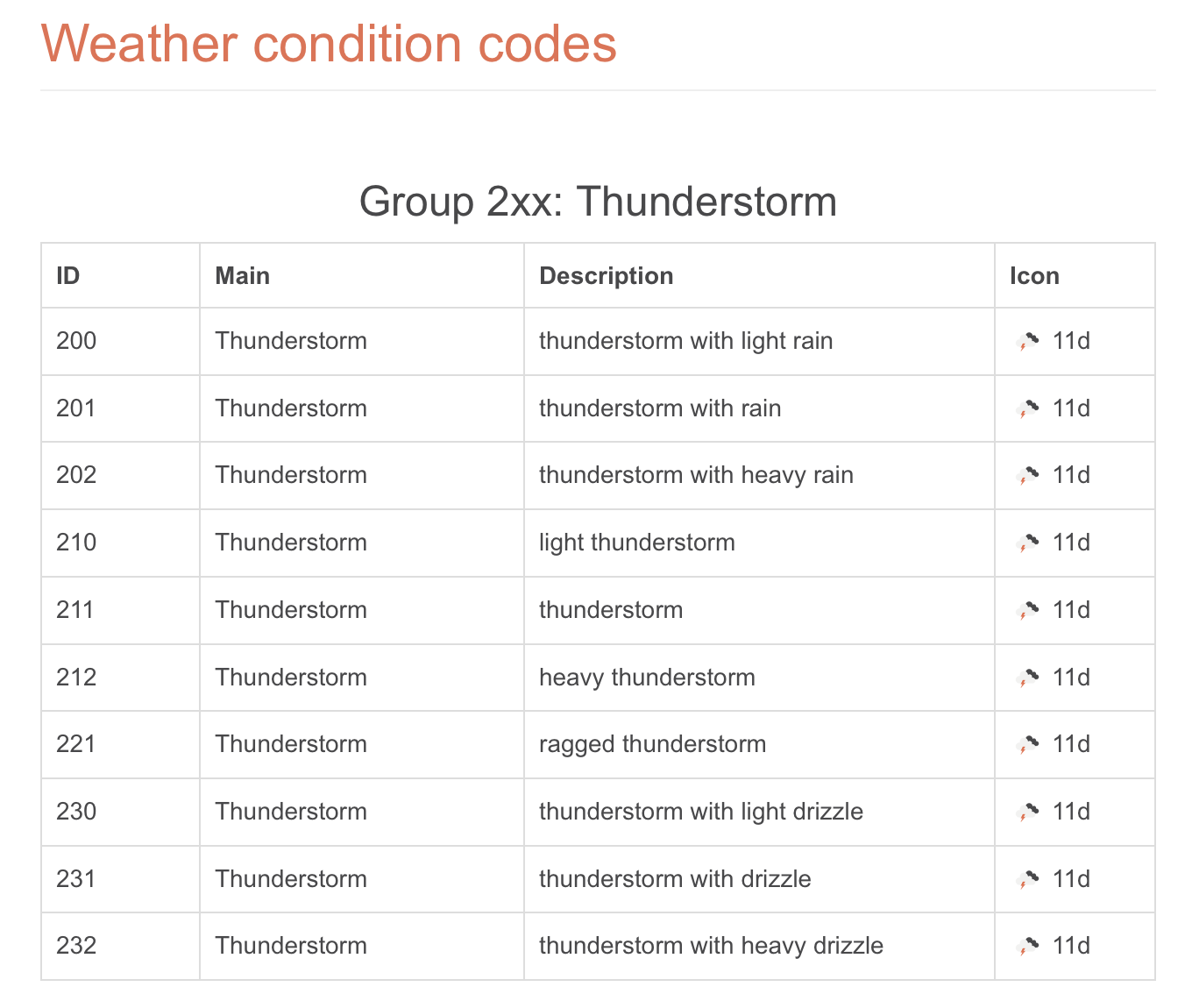
Weather condition codes
Weather Conditions - OpenWeatherMap
Weather Conditions Home Weather Conditions
openweathermap.org
WeatherData.swift
| importFoundation struct WeatherData: Decodable { let name: String let main: Main let weather: [Weather] } struct Main: Decodable { let temp: Double } struct Weather: Decodable { let id: Int let description: String } |
지난 게시글에서 만들었던
json의 리스트 중 id를 추가해보자.

이렇게 결과를 받을 수 있다.

API 문서에 따르면 502는 위와 같다.
이 id에 따라 날씨 상태를 정의하는 Switch 문을 만들어본다.
WeatherManager.swift
| func parseJSON(weatherData: Data) { let decoder = JSONDecoder() do{ let decodedData = trydecoder.decode(WeatherData.self, from: weatherData) print("decodedData.name: \(decodedData.name)") print("decodedData.main.temp: \(decodedData.main.temp)") print("decodedData.weather[0].id: \(decodedData.weather[0].id)") print("decodedData.weather[0].description: \(decodedData.weather[0].description)") let id = decodedData.weather[0].id print(getConditionName(weatherId: id)) } catch{ print(error) } } func getConditionName(weatherId: Int) -> String { switch weatherId { case2 00...232: return"cloud.bolt" case 300...321: return "cloud.drizzle" case 500...531: return"cloud.rain" case 600...622: return"cloud.snow" case 701...781: return"cloud.fog" case 800: return"sun.max" case 801...804: return"cloud.bolt" default: return"cloud" } } |
여기서 MVC 디자인 패턴을 적용하고 가자.
우선 Model 폴더에 WeatherModel.swift 파일을 생성한다.
WeatherModel.swift
| import Foundation struct WeatherModel { let conditionId: Int let cityName: String let temperature: Double func getConditionName(weatherId: Int) -> String { switch weatherId { case 200...232: return"cloud.bolt" case 300...321: return "cloud.drizzle" case 500...531: return"cloud.rain" case 600...622: return"cloud.snow" case 701...781: return"cloud.fog" case 800: return"sun.max" case 801...804: return"cloud.bolt" default: return"cloud" } } } |
WeatherManager.swift
| func parseJSON(weatherData: Data) { let decoder = JSONDecoder() do{ let decodedData = try decoder.decode(WeatherData.self, from: weatherData) let id = decodedData.weather[0].id let name = decodedData.name let temp = decodedData.main.temp let weather = WeatherModel(conditionId: id, cityName: name, temperature: temp) } catch { print(error) } } |
Computed Properties
다시 아래 스크립트를 더 간단히 조건식이 들어간 var 변수로 만들어준다.
이런 변수를 Computed property라고라고 한다.
WeatherModel.swift
| struct WeatherModel { let conditionId: Int let cityName: String let temperature: Double // conditionId가 200~232면 conditionName = "cloud.bolt" var conditionName: String { switch conditionId{ case 200...232: return"cloud.bolt" case 300...321: return "cloud.drizzle" case 500...531: return"cloud.rain" case 600...622: return"cloud.snow" case 701...781: return"cloud.fog" case 800: return"sun.max" case 801...804: return"cloud.bolt" default: return"cloud" } } } |
그리고 WeatherManager.swift 스크립트를 아래와 같이 바꿔준다.
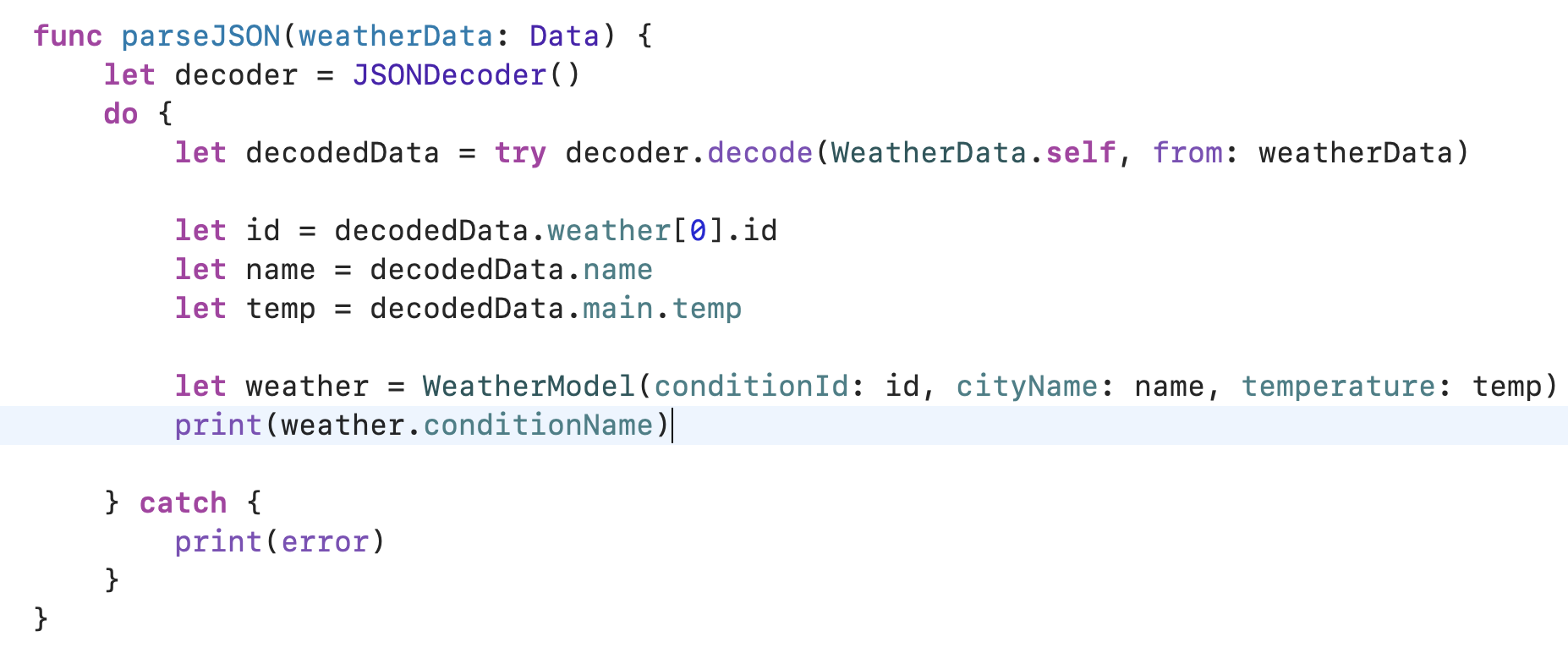
MVC 디자인 패턴으로 코드는 더욱 더 간결해지고
이해하기 쉬워졌다.
이를 'Refactoring' 이라고 한다.
Computed Properties를 더 이해하기 위해
온도를 받아와서 소수점 한자리로 나오는 var 변수를 만들어보자.
| let temperature: Double var temperatureString: String { return String(format: "%.1f", temperature) } |
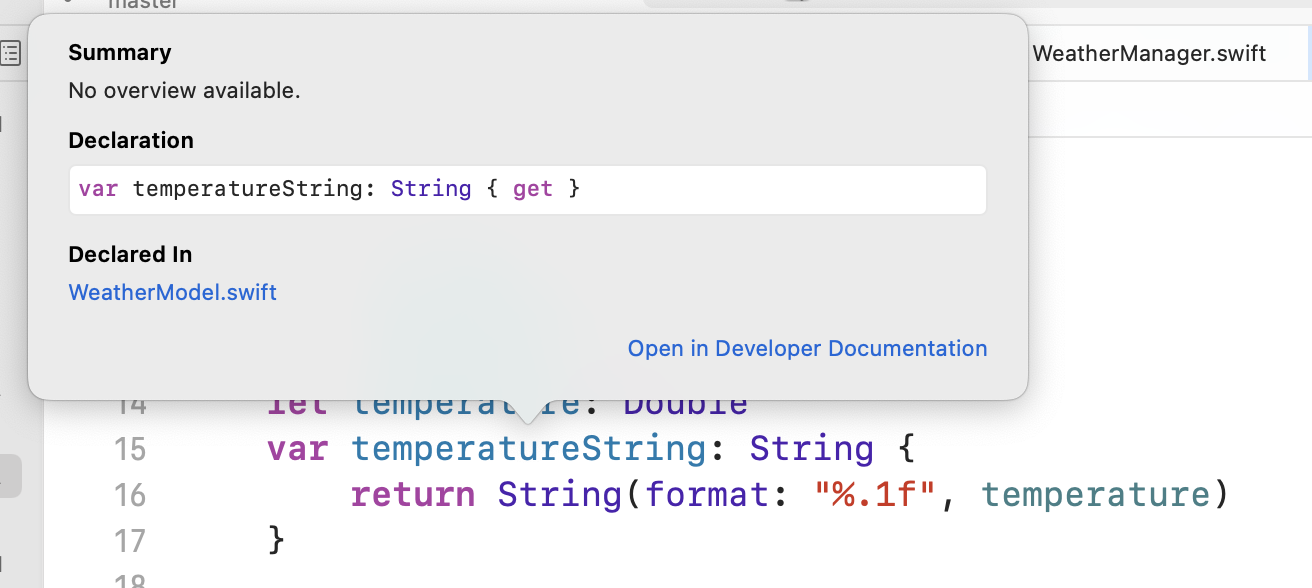
아래 이미지를 보면 { get } 이라고 나오는데
이게 computed properties를 의미하나보다.
이전에 유니티할때 get, set 변수들 정말 많이 봤는데
이제야제대로 된 의미를 조금 이해하고 있다.
참고
안젤라유 강의: https://www.udemy.com/course/ios-13-app-development-bootcamp/
iOS & Swift - The Complete iOS App Development Bootcamp
From Beginner to iOS App Developer with Just One Course! Fully Updated with a Comprehensive Module Dedicated to SwiftUI!
www.udemy.com
'iOS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| iOS (Swift) 예시로 쉽게 이해하는 Extension (0) | 2022.06.27 |
|---|---|
| iOS (Swift) Internal & External Parameter 란? (0) | 2022.06.26 |
| iOS (Swift) JSON 디코딩(Decoding) (0) | 2022.06.24 |
| iOS (Swift) Closure 의 개념과 사용 방법 (0) | 2022.06.23 |
| iOS (Swift) URL Session for Networking (0) | 2022.06.22 |




